You have an outstanding SaaS product with features that provide great value to your customers. But how do you price the product to remain competitive yet not compromise with profits?
We get it, pricing is hard; you do not want to scare off your prospects by setting the pricing too high. You also do not want to leave money on the table by pricing your product too low. After all, you want to be compensated fairly for your hard work and the value your customers get out of your product.
Setting an optimal pricing strategy is a very important step for any SaaS business. A complicated pricing model can confuse your customers and be a cause for customer churn in the future. So it's always advisable you provide a clear idea of your product features and how much your customers are paying for it.
Before you set up a pricing model, it is ideal to perform a comprehensive analysis of your business model and answer the following questions:
- Who is your ideal customer?
- How much is your target customer willing to pay for your product?
- How do you want to position your product?
- What is your competitive advantage?
- How important is repeat business?
Now that you have answered these questions, let's dive into the different models available to you to monetize your product.
Whether you are setting up your pricing for the first time or revisiting your old strategy, this quick guide will help you understand the basics of SaaS pricing models and identify the best ways to market and grow your business.
There are several types of pricing strategies to choose from depending on your business, your product features, and use cases. In this guide, we will look at the different pricing models and their pros and cons.
Usage-based pricing model
Usage-based pricing or pay-as-you-go pricing model is dynamic pricing that is configured based on how much usage is consumed. This model is often used by businesses that charge their customers based on the number of API requests performed, transactions processed, bandwidth used, or a percentage of revenue made.
Pros
- No upfront costs, so even small businesses or startups can use your product as the pricing is calculated based on their usage
- The pricing scales with the customer. An increase in usage leads to an increased price - ensuring that the pricing is fair.
Cons
- Can cause uncertainties. Customers cannot calculate their costs in advance. Businesses can't predict revenue as billing varies month to month.
- You cannot charge fees based on the size of the organization. So there may be chances that an enterprise-level organization is paying lower than a smaller-sized business.
Usage-based Pricing Example
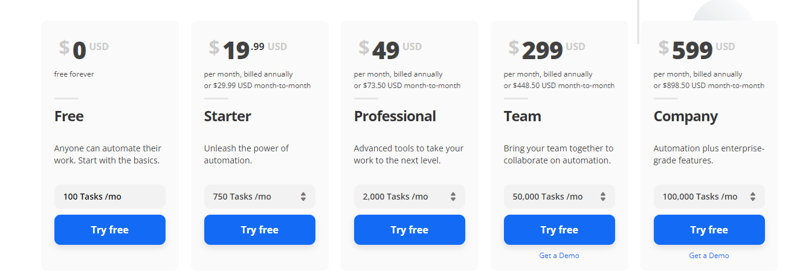
This pricing method is commonly used by SaaS and IoT companies. Zapier has a usage-based pricing model where people are charged based on the number of “Zaps” or tasks they use.
Flat rate pricing model
The flat-rate pricing model is a one size fits all pricing strategy where customers are charged a fixed amount monthly, quarterly, or annually depending on their chosen subscription package. This is one of the simplest SaaS pricing strategies: everyone gets the same features and pays the same price.
Pros
- Easy to sell and explain the pricing model to customers
- It's easier to forecast revenue and customer churn
- It's much simpler to create a marketing plan for a flat-rate pricing model compared to creating a plan for different package levels
Cons
- It's tricky to set a price that is attractive to smaller businesses while making enough profits for charging enterprise level accounts
- You cannot charge more for providing a better value
- Unlike other pricing models, you do not get the opportunity to update your pricing to reflect usage as the customers scale their business.
- Some may overuse your system cutting into your flat rate margins.
Flat-rate pricing example
Basecamp, a remote working tool uses the flat-rate pricing model effectively by clearly explaining its simple pricing strategy.

Tiered pricing model
This is one of the best, and most commonly used B2B SaaS pricing models. With tiered pricing, you can offer different packages, with separate features, customization, and pricing for each level. The pricing also differs depending on product usage or the number of users allowed to access the digital product.
This model offers multiple tiers to choose from and works for both small businesses and startups and enterprise-level accounts. Tiered pricing allows you to tailor the pricing based on different customer personas.
Pros
- This pricing model leads to higher conversion rates as it's highly targeted based on customer personas
- Ability to upsell customers from a lower tier to a higher tier
Cons
- The different levels and features can confuse prospective customers
- Businesses often risk overcomplicating the tiers and confusing potential customers
Tiered Pricing Model Example
Hubspot has a tiered pricing model and there is a big jump in pricing each time you get to a higher tier. The software is priced to be used by small businesses all the way up to enterprise-grade teams.
Per-user pricing model
The per-user pricing model as the name suggests charges businesses based on the total number of users that are registered to use the software. This pricing strategy is simple and easy to adopt, so it's one of the most commonly used models by SaaS businesses. With per-user pricing, you can easily forecast recurring revenue as it charges each user account.
Pros
- It's a simple pricing model. Customers find it easy to use and predict future costs.
- This pricing model makes it easier for salespeople to pitch the product as well as predict revenue
Cons
- Customers often resist adding new users as it means incurring extra costs. This can limit the growth of your business.
- The pricing doesn’t reflect the value you provide to your customers
Per-User Model example
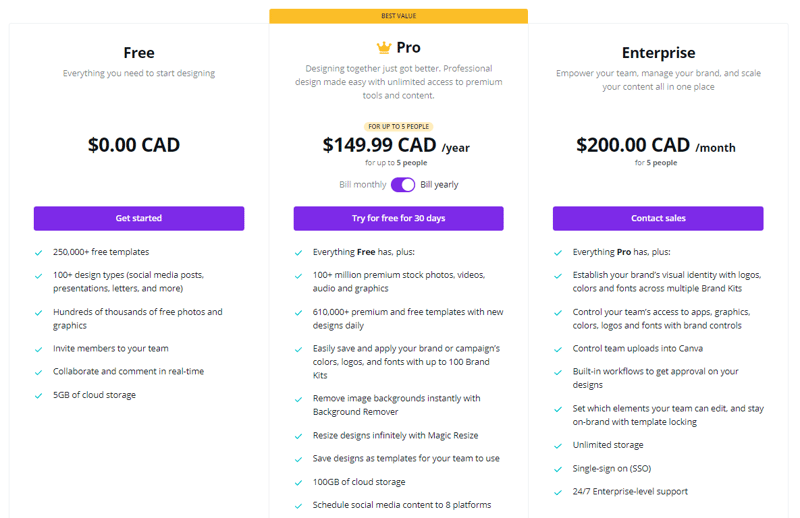
Canva charges on a per-user basis. They have three packages wherein each package comes with additional features.
Freemium pricing model
Freemium model is a common SaaS product pricing strategy where you let customers use certain features of your product for free. This is a great marketing and lead generation tool for your business.
The freemium model is used as a part of the tiered pricing model, allowing potential customers to first use the product for free before upgrading to the paid version of the package. If your product provides great value, your customers will likely upgrade to the paid version.
Several leading SaaS companies like Dropbox, Slack, Zapier, etc. use the freemium model to allow potential customers to experience the product before paying for it.
Pros
- This model makes it easy for customers to try the product
- With no upfront costs, it's easier for customers to adopt this model
- It's a great marketing tool and solves the problem of the is initial adoption of your product
Cons
- The number of people that convert to paid users can be incredibly low
- It lowers the value of your product in the eyes of your customers when they have to pay for the product
Freemium Pricing Model example
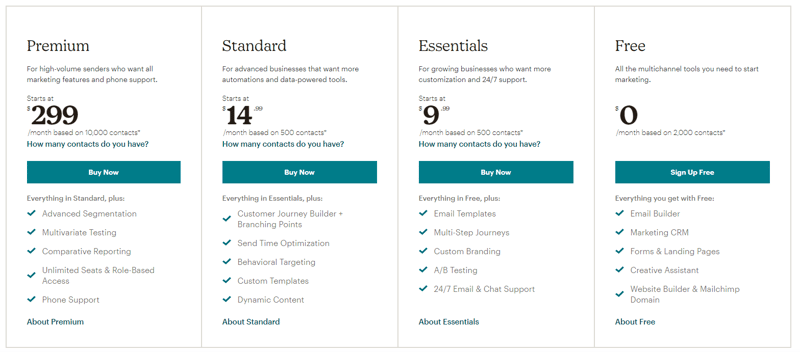
Mailchimp offers a free version which they offer to accounts with less than 20,000 contacts. The freemium model acts as a lead magnet and allows the company to acquire and grow users before they can grow in size and are ready to become paid users.
Conclusion
Now that you have some insights into the different strategies for pricing a SaaS product, you are better positioned to analyze and understand which one is best suited for your business.
As you may have already noticed, all the pricing models discussed in this guide have both pros and cons. Some of them may be more suitable for your business now. As you grow and scale your business, a different pricing strategy may be more effective for you. So, it is always advisable to evaluate and revisit your pricing strategy every few years whether you are a SaaS startup or a large organization,
Here are 3 key takeaways we would like you to remember about SaaS platform pricing -
- Do not set up your pricing and forget about it. Be sure to revisit and update your pricing to ensure it still matches your business model.
- As you scale your business, your pricing should reflect that. Price your product based on the value it provides to your target customer.
- Keep your pricing simple and easy to adapt
We hope that you found this guide helpful and are closer to finding the best SaaS pricing model for your business.
About the Author
Ryan Susanna /
Ryan is a seasoned telecommunications expert with a broad background in both the service provider and software vendor sides of the business. Ryan is currently responsible for worldwide sales at LogiSense. During his tenure, Ryan has held executive level positions including Senior Sales Executive, and Director of Sales. In these roles, he has provided strategic sales, product, and market guidance for our next generation IP service management solutions.
